Education for girls. Microloans for women. Two tools with one goal:
An end to poverty.
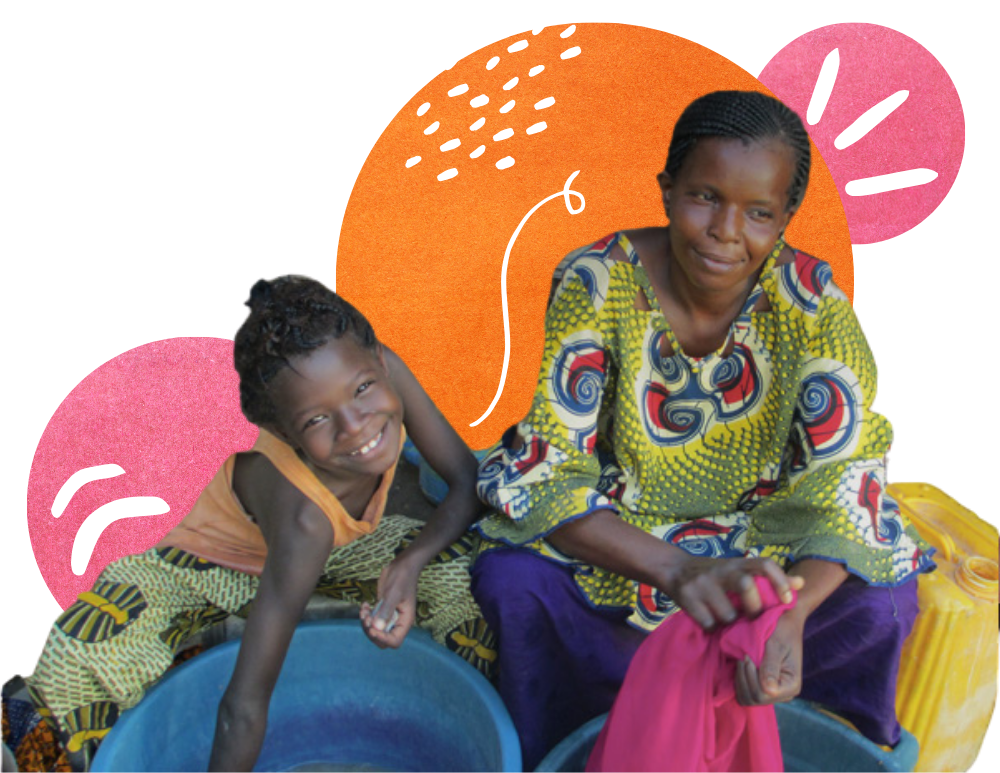
Worldwide, 119 million girls are out of school.
Girls to School is addressing this injustice in West Africa by working with non-governmental organization in West Africa that create opportunities for girls to obtain a quality education, and women to obtain access to credit to catalyze income-generating activities.


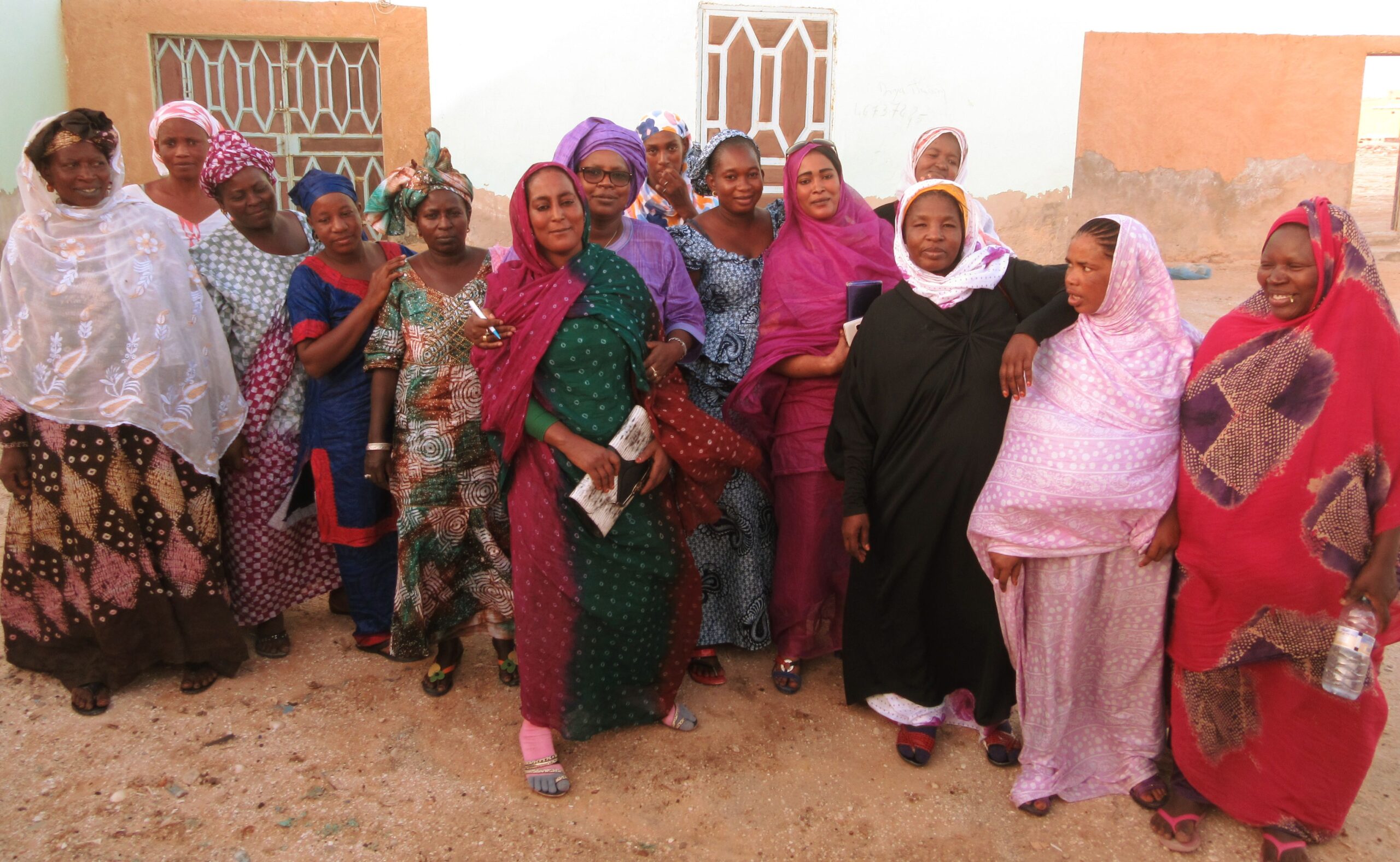
Our partner organization is Amenons Nos Filles a l’Ecole – ANFE (Bringing Our Girls to School).
We are proud to support the critical work of this group in Mauritania.
We focus on three signature programs:
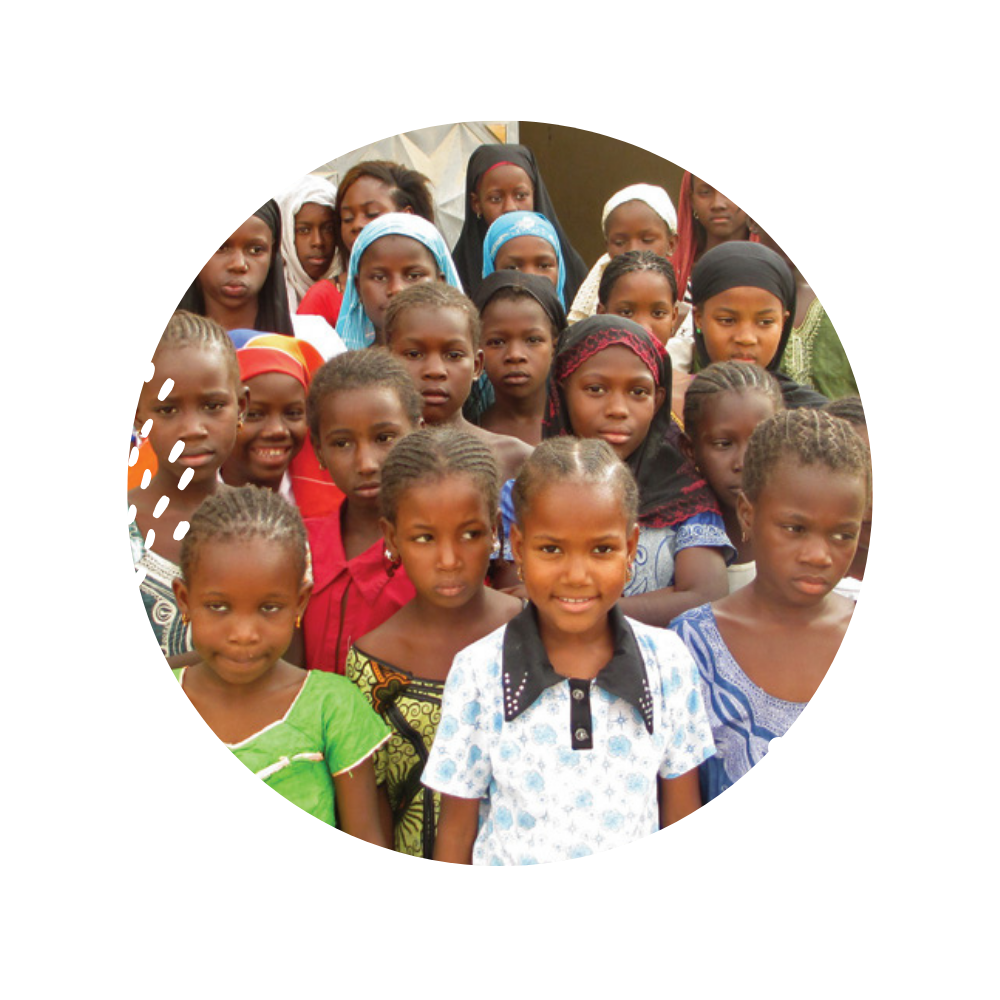

Girls’ Education Opportunities
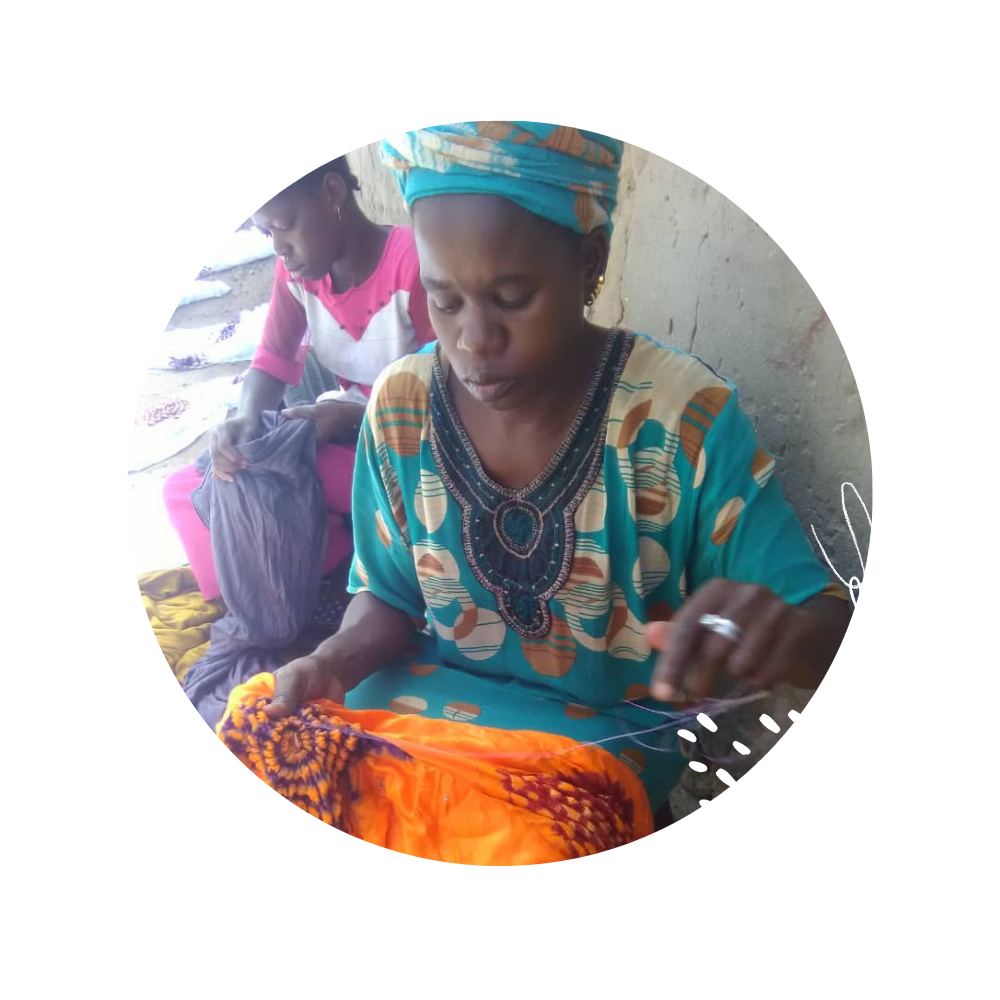

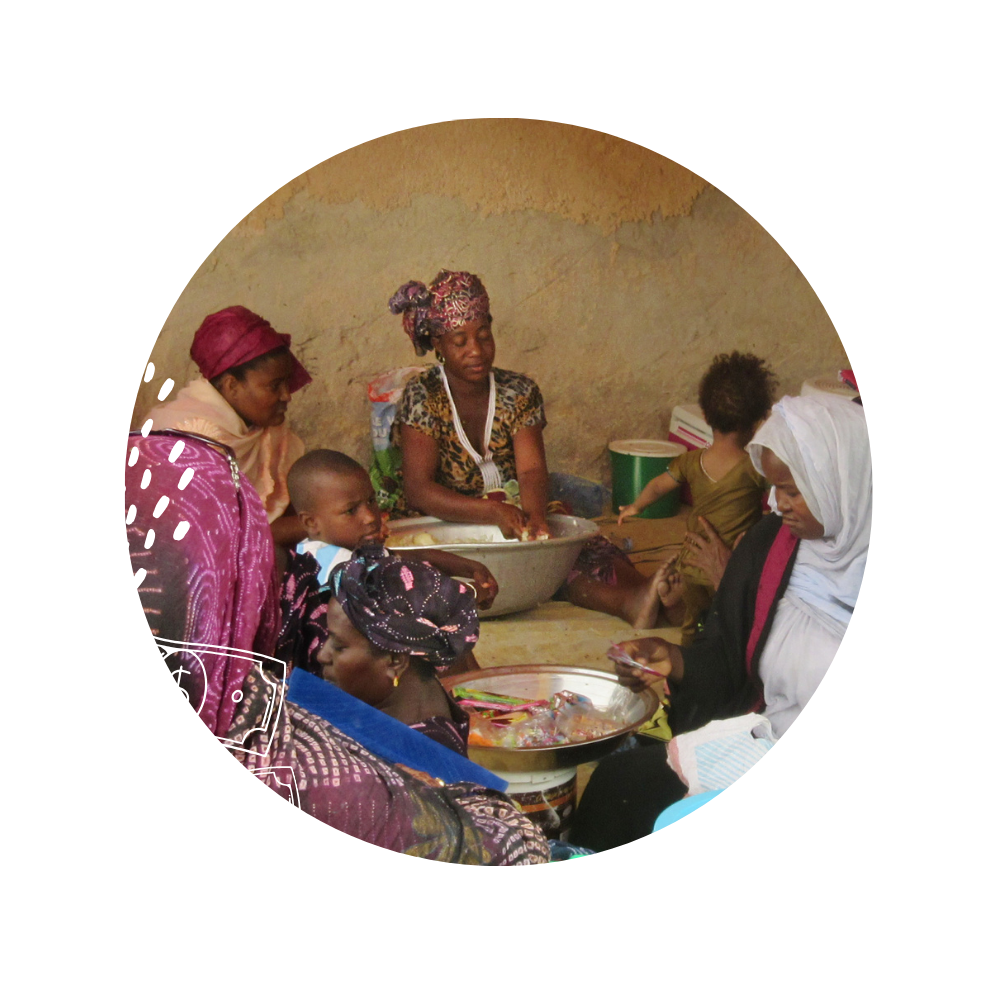
Microfinance & Entrepreneurtship

